- CNC as a manufacturing vanguard
- Which is better - CNC or 3D printing?
- Will 3D Printing ever replace CNC?
- When to use CNC and when to use 3D printing?
- Manufacturing on Treatstock
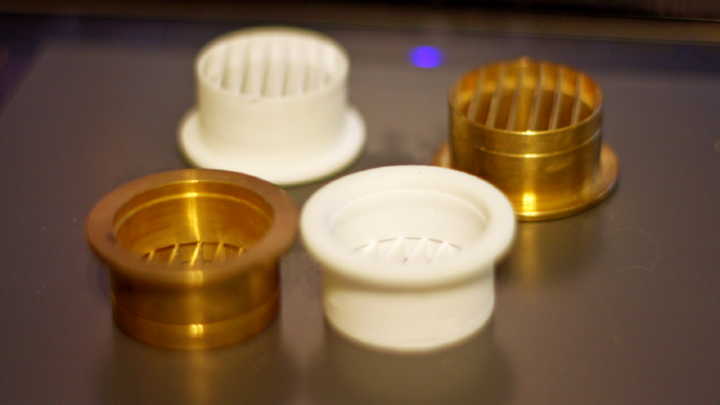
CNC (computer numerical control) and 3D printing are the two leading manufacturing technologies used for rapid prototyping and low-volume production, but use completely different production techniques to achieve the result. CNC uses subtractive methods which involves removing unnecessary parts from a block of material, whereas 3D printing employs additive methods by starting with a blank canvas and using materials to build a product layer by layer.
Both manufacturing technologies pose advantages and disadvantages and it can be difficult to understand which one should be implemented in your project and when. It’s important to note that when it comes to mass production, for instance, more than 200 parts, other manufacturing technologies such as injection molding are likely to be more suitable and much more cost-effective. We have prepared this guide to provide a comparative analysis of CNC and 3D printing, so you can see all the ins and outs of each method and to help you with your decision-making process.
CNC as a manufacturing vanguard
CNC is a collective name for a wide range of technologies that are used for manufacturing worldwide. Frankly speaking, subtractive manufacturing methods are much more popular and offer greater versatility compared to other manufacturing processes. Usually, when one needs a fully functional prototype, part or detail, CNC technology is the primary tool that is used. It‘s frequently used for engineering evaluations and testing. Using military terminology, subtractive manufacturing can be called vanguard and additive manufacturing a rearguard, with the latter used when help is needed. Reading this guide, you can learn why one technique may be more preferable over the other and why both of them are so required in the modern manufacturing industry.
Which is better - CNC or 3D printing?
1. Range of applications
| CNC | 3D Printing |
| Usually, CNC machines are used for making durable, precise, and heat-resistant parts. CNC machines can be found in nearly every industry, from little businesses to huge production factories. The range of applications for the technology is huge, including jewelry, metal molding, casting, and more. | The range of applications for 3D printing is somewhat unbelievable and captures everyone’s imagination. Among the fields of applications are mechanical engineering, jewelry, aerospace, healthcare, and even exotic uses such as printing food, bio-printing and building construction. |
2. Various materials | |
| CNC | 3D Printing |
| CNC works with a vast variety of materials such as metal alloys, plastic, jewelry wax and many others. Moreover, CNC is the main manufacturing tool for wood processing, and is also capable of quick and precise work with other materials too. One of the main advantages of CNC manufacturing is that it can be used for almost any solid substance. | A variety of materials that are available for 3D printing is almost as big as for CNC. Among them are various plastics and metal alloys including those that are very hard for machining. However, 3D printers that are capable of manufacturing metals are quite expensive. |
3. Waste | |
| CNC | 3D Printing |
| Usually, CNC machines are used for making durable, precise, and heat-resistant parts. CNC machines can be found in nearly every industry, from little businesses to huge production factories. The range of applications for the technology is huge, including jewelry, metal molding, casting, and more. | On the contrary to subtractive methods, 3D printing in most case uses the exact amount of material that is needed for the manufacturing of an object and produces minimal waste. However, you shouldn’t forget about the materials that are spent on creating support structures (though metal 3D printing doesn’t need them). |
4. Operating Costs | |
| CNC | 3D Printing |
| Usually, consumables and materials for CNC machines are much cheaper than those for the 3D printer. However, CNC requires trained specialists to pre-program the processing parameters and tool paths. That means extra time and money that is included in the cost of the final product. That’s why in spite of a relatively fast manufacturing speed, in some cases, 3D printing is more preferable. | The entry level costs with 3D printing is much cheaper and faster than with any other technology. However, consumables and materials can be much more expensive in comparison to CNC. Overall, additive manufacturing is more advantageous for a limited volume of unique objects, but for more than 20 units, it’s more profitable to use CNC or other methods. |
5. Various tools | |
| CNC | 3D Printing |
| It’s possible to use various tools within the same machine which broadens the opportunities and makes CNC such a versatile technology. Some machines are capable of changing tools automatically according to the current task, so the manufacturing process doesn’t have extended breaks. | In case of 3D printing, the number of available tools is quite limited. Sometimes it can be a problem, but usually, when 3D printing is applied, other methods are not necessary at all. The diversity of 3D printing machines is quite incredible and seems that there is no problem that can’t be solved with additive manufacturing. |
6. Precision | |
| CNC | 3D Printing |
| CNC processes are among the leaders in both speed and precision. It’s positional accuracy and tolerance is unrivaled (accuracy of CNC machining is approximately 0.01mm - 0.05mm depending on geometry). Moreover, surface quality is also quite impressive as well. Some CNC machines can carry out extremely tricky tasks and projects where precision within microns is needed. However, incorrect usage can damage tools and cause defected parts. That’s why it’s always important to work only with highly-qualified specialists. | Resolution of 3D printers as well as the surface quality is not as good in comparison to CNC (approximate layer thickness for 3D printing is between 0.1mm – 0.5mm). It’s important to note that the speed of manufacturing dramatically varies depending on the precision required. Nevertheless, most 3D printer users don’t need high accuracy. Therefore, the advantages of additive manufacturing compensate limitations. |
7. Speed | |
| CNC | 3D Printing |
| Depending on the complexity of the design and the chosen material, the speed of manufacturing can be unbelievably fast and in some cases even unrivaled. However, you should keep in mind that pre-programing process also can take up a lot of time, especially in case of tricky projects. Turnaround time for CNC machining takes 3-4 days (for 3D printing it’s approximately 1-2 days). | The additive manufacturing process can be slow, sometimes even extremely slow. That’s why it’s not the best choice for serial production. So why is 3D printing considered as rapid prototyping? The reason is quite simple - the 3D printer doesn’t require lengthy pre-programming before firing it up, all it needs is to load the material and to slice the files which can be done in minutes before sending it to the 3D printer. Besides, additive manufacturing is improving every day and the speed of the latest machines are several times faster than its predecessors. |
8. Post-processing | |
| CNC | 3D Printing |
| Sometimes a detail made with CNC requires post-processing (grinding and sanding) after machining, but more often than not, it’s surface is good enough for use as it is. Moreover, parts can be sanded and finished on the same machine. CNC processed parts can be as good as casts. | In case of additive manufacturing, printed products generally require post-processing, especially for the temperature processing of metal parts that have internal stress. At the same time, printed parts are usually ready to use right away. |
9. 3D models and software | |
| CNC | 3D Printing |
| Software preparation is usually much more complicated for CNC processes than for 3D printing. It’s necessary to generate tool paths with computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software. A specialist must specify dimensions and location of the stock material, characteristics of the cutter, speeds for the axes, and spindle.. | Generally speaking, 3D printers are much more accessible. A special software called a slicer is used for transferring a digital model in a G-code that controls the manufacturing process of a 3D printer. The method of slicing is much easier than pre-programming a CNC machine. |
Will 3D Printing ever replace CNC?
Since the 1940s, CNC machining remains the most common mean of prototyping until today. But what’s going to happen tomorrow? Can 3D printing overtake CNC? The answer is YES and NO. From one side, 3D printing has already occupied a part of tasks that were previously done by CNC, but it’s just the tiny part. Besides, as we stated before, the CNC processes is usually much more affordable than 3D printing. One could say that CNC machining is at the zenith of its development. Some industrial CNC machines are like themselves a mini factory with their size and enormous capabilities. They can fulfill an outstanding number of tasks. However, they have their limitations. Fortunately, additive manufacturing is here to save the day when CNC fails us. Additive manufacturing captures the imagination when one can see the variety of methods and applications where it used. Using a 3D printer, it’s possible to manufacture almost any object from scratch in a matter of days. In some cases, subtractive and additive manufacturing can overlap, however, each of them has advantages and disadvantages.
When to use CNC and when to use 3D printing?
The choice of technology should be determined based on its application. If you are not sure, then there is a straightforward recommendation: when it’s possible to use CNC - use CNC, otherwise use 3D printing. In some cases, it may even be more beneficial to combine both additive and subtractive manufacturing process to complete an end goal. For instance, SLA and SLS 3D printing could be used as a preparatory stage for CNC machining. 3D printing is mostly applied when traditional methods are not possible to use, or materials cannot be easily machined, like alloys containing hard metal. Subtractive and additive manufacturing could be compared to a fork and knife, as both of them can be used individually for specific purposes but are more effective when combined together. That’s why hybrid machines that combine the main features of both methods are so popular nowadays. The multifunctional system can replace 3D printers and CNC machines at the same time. There are relatively affordable desktop machines or expensive industrial ones that are worth hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Manufacturing on Treatstock
In the world of industrial manufacturing, it can be convenient to have quick and easy access to both CNC and 3D printing and all this is possible on Treatstock. In just a few clicks, you can browse thousands of manufacturers from all over the world and place an order within minutes.
3D printing servicesMachining services